Difference between revisions of "Raspberry Pi Compute Dev Kit - BCM2835 32Bits ARM"
(→Specification) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
So if you are going to create your own PCB, this kit must be your best choice. | So if you are going to create your own PCB, this kit must be your best choice. | ||
| − | == | + | ==Features== |
*Full flexibility of the BCM2835 SoC | *Full flexibility of the BCM2835 SoC | ||
*many more GPIOs and interfaces are available as compared to the Raspberry Pi | *many more GPIOs and interfaces are available as compared to the Raspberry Pi | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
*Large Range of GPIOs & Interfaces | *Large Range of GPIOs & Interfaces | ||
*On board 4GB eMMC Flash memory | *On board 4GB eMMC Flash memory | ||
| − | == | + | ==Specifications== |
*BCM2835 processor and 512Mbyte of RAM | *BCM2835 processor and 512Mbyte of RAM | ||
*67.6x30mm board | *67.6x30mm board | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
*Micro USB power connector | *Micro USB power connector | ||
| − | ==Hardware | + | ==Hardware resources== |
[[File:Raspberry Compute Modules.jpg|700px|]] | [[File:Raspberry Compute Modules.jpg|700px|]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Power Supply== |
The Compute Module has six separate supplies that must be present and powered at all times; you cannot leave any of them unpowered, even if a specific interface or GPIO bank is unused. The six supplies are as follows: | The Compute Module has six separate supplies that must be present and powered at all times; you cannot leave any of them unpowered, even if a specific interface or GPIO bank is unused. The six supplies are as follows: | ||
*VBAT powers the BCM2835 processor core. It feeds the SMPS that generates the chip core voltage. | *VBAT powers the BCM2835 processor core. It feeds the SMPS that generates the chip core voltage. | ||
Revision as of 03:07, 6 August 2014
Introduction
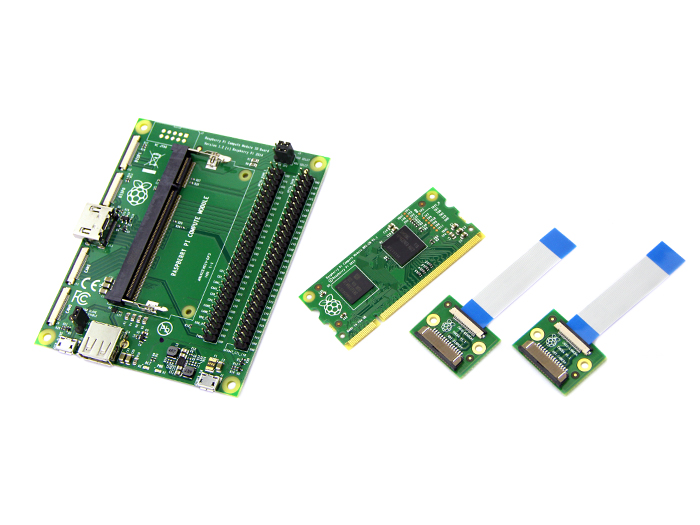
Sometimes the Raspberry Pi seems too big for us if we don’t have much room for it. At this time, we may desire for a smaller Pi. The Raspberry Pi compute module is a small compact module which has the same key ingredients and performance as a regular Pi. It’s so slim that can fit into a DDR2 memory slot. The compute module contains the BCM2835 processor and 512Mbyte of RAM as well as a 4Gbyte eMMC Flash device. This module is designed for people who want to create their own PCB. The compute module IO board is a board produced for the compute module. The board provides the power to the module, the HDMI and USB connectors to make up an entire system. You can program the module’s Flash memory; access the interfaces via the board. So if you are going to create your own PCB, this kit must be your best choice.
Features
- Full flexibility of the BCM2835 SoC
- many more GPIOs and interfaces are available as compared to the Raspberry Pi
- 32 bits
- Flexible & Rapid Prototype Development
- Aimed at business and industrial users
- Large Range of GPIOs & Interfaces
- On board 4GB eMMC Flash memory
Specifications
- BCM2835 processor and 512Mbyte of RAM
- 67.6x30mm board
- 4GB of eMMC Flash
- micro USB connector type B
- 2 x CSI ports for camera boards
- 2 x DSI ports for display boards
- standard DDR2 SODIMM connector
- Full size HDMI port
- Micro USB power connector
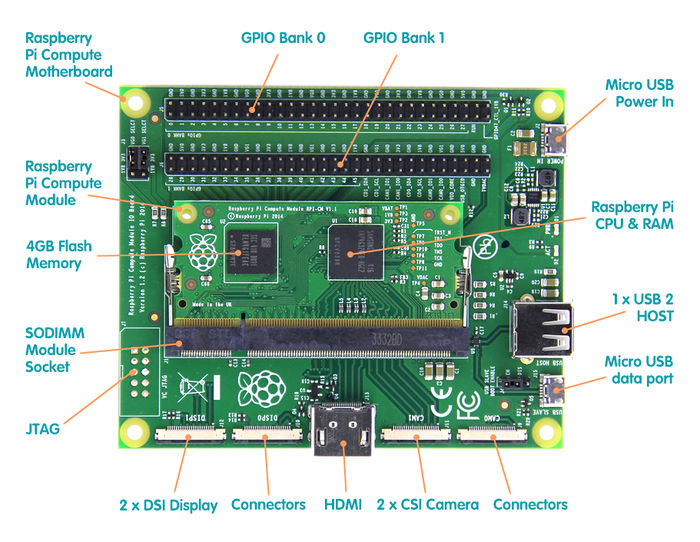
Hardware resources
Power Supply
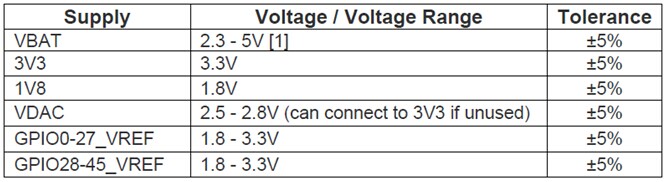
The Compute Module has six separate supplies that must be present and powered at all times; you cannot leave any of them unpowered, even if a specific interface or GPIO bank is unused. The six supplies are as follows:
- VBAT powers the BCM2835 processor core. It feeds the SMPS that generates the chip core voltage.
- 3V3 powers various BCM2835 PHYs, IO and the eMMC Flash memory.
- 1V8 powers various BCM2835 PHYs, IO and SDRAM.
- VDAC powers the composite (TV-out) DAC.
- GPIO0-27_VREF powers the GPIO 0-27 IO bank.
- GPIO28-45_VREF powers the GPIO 28-45 IO bank.
Note that the voltage range for best SMPS efficiency is ~3.3 - 4.3V.
Resource
Instruction Media:Rpicomputemodulesinstruction.pdf
Schematic Media:Rpicomputemodulesschematic.pdf