Difference between revisions of "ADXL335 Triple Axis Accelerometer Breakout"
(→Usage) |
(→Example code) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
const int ypin = A2; // y-axis | const int ypin = A2; // y-axis | ||
const int zpin = A3; // z-axis (only on 3-axis models) | const int zpin = A3; // z-axis (only on 3-axis models) | ||
| − | + | // | |
int sampleDelay = 500; //number of milliseconds between readings | int sampleDelay = 500; //number of milliseconds between readings | ||
void setup() | void setup() | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
// initialize the serial communications: | // initialize the serial communications: | ||
Serial.begin(9600); | Serial.begin(9600); | ||
| − | + | // | |
//Make sure the analog-to-digital converter takes its reference voltage from | //Make sure the analog-to-digital converter takes its reference voltage from | ||
// the AREF pin | // the AREF pin | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
{ | { | ||
int x = analogRead(xpin); | int x = analogRead(xpin); | ||
| − | + | // | |
//add a small delay between pin readings. I read that you should | //add a small delay between pin readings. I read that you should | ||
//do this but haven't tested the importance | //do this but haven't tested the importance | ||
delay(1); | delay(1); | ||
| − | + | // | |
int y = analogRead(ypin); | int y = analogRead(ypin); | ||
| − | + | // | |
//add a small delay between pin readings. I read that you should | //add a small delay between pin readings. I read that you should | ||
//do this but haven't tested the importance | //do this but haven't tested the importance | ||
delay(1); | delay(1); | ||
| − | + | // | |
int z = analogRead(zpin); | int z = analogRead(zpin); | ||
| − | + | // | |
//zero_G is the reading we expect from the sensor when it detects | //zero_G is the reading we expect from the sensor when it detects | ||
//no acceleration. Subtract this value from the sensor reading to | //no acceleration. Subtract this value from the sensor reading to | ||
//get a shifted sensor reading. | //get a shifted sensor reading. | ||
float zero_G = 512.0; | float zero_G = 512.0; | ||
| − | + | // | |
//scale is the number of units we expect the sensor reading to | //scale is the number of units we expect the sensor reading to | ||
//change when the acceleration along an axis changes by 1G. | //change when the acceleration along an axis changes by 1G. | ||
//Divide the shifted sensor reading by scale to get acceleration in Gs. | //Divide the shifted sensor reading by scale to get acceleration in Gs. | ||
float scale = 102.3; | float scale = 102.3; | ||
| − | + | // | |
Serial.print(((float)x - zero_G)/scale); | Serial.print(((float)x - zero_G)/scale); | ||
Serial.print("\t"); | Serial.print("\t"); | ||
| − | + | // | |
Serial.print(((float)y - zero_G)/scale); | Serial.print(((float)y - zero_G)/scale); | ||
Serial.print("\t"); | Serial.print("\t"); | ||
| − | + | // | |
Serial.print(((float)z - zero_G)/scale); | Serial.print(((float)z - zero_G)/scale); | ||
Serial.print("\n"); | Serial.print("\n"); | ||
| − | + | // | |
// delay before next reading: | // delay before next reading: | ||
delay(sampleDelay); | delay(sampleDelay); | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
==How to buy== | ==How to buy== | ||
Click here to buy [ADXl335 3 axis accelormeter module] | Click here to buy [ADXl335 3 axis accelormeter module] | ||
Revision as of 09:41, 22 May 2012
Introduction
This is a breakout board for Analog Devices analog 3 axis accelormeter. The ADXL335 is a small, thin, low power, complete 3-axis accel-erometer with signal conditioned voltage outputs. The product measures acceleration with a minimum full-scale range of ±3 g. It can measure the static acceleration of gravity in tilt-sensing applications, as well as dynamic acceleration resulting from motion, shock, or vibration. The user selects the bandwidth of the accelerometer using the CX, CY, and CZ capacitors at the XOUT, YOUT, and ZOUT pins. Bandwidths can be selected to suit the application, with a range of 0.5 Hz to 1600 Hz for the X and Y axes, and a range of 0.5 Hz to 550 Hz for the Z axis.
Features
- 3-axis sensing
- full-scale range of ±3 g
- Low power : 350 μA (typical)
- Single-supply operation: 1.8 V to 3.6 V
- 10,000 g shock survival
- Excellent temperature stability
- BW adjustment with a single capacitor per axis
- RoHS/WEEE lead-free compliant
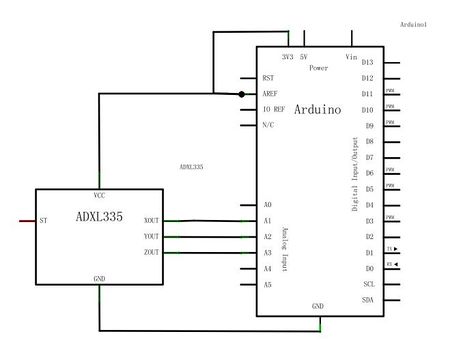
Usage
Here is the guide illustrates how to connect an Arduino to the ADXL335 breakout board. The following is a table describing which pins on the Arduino should be connected to the pins on the accelerometer:
Example code
// these constants describe the pins. They won't change:
const int xpin = A1; // x-axis of the accelerometer
const int ypin = A2; // y-axis
const int zpin = A3; // z-axis (only on 3-axis models)
//
int sampleDelay = 500; //number of milliseconds between readings
void setup()
{
// initialize the serial communications:
Serial.begin(9600);
//
//Make sure the analog-to-digital converter takes its reference voltage from
// the AREF pin
pinMode(xpin, INPUT);
pinMode(ypin, INPUT);
pinMode(zpin, INPUT);
}
void loop()
{
int x = analogRead(xpin);
//
//add a small delay between pin readings. I read that you should
//do this but haven't tested the importance
delay(1);
//
int y = analogRead(ypin);
//
//add a small delay between pin readings. I read that you should
//do this but haven't tested the importance
delay(1);
//
int z = analogRead(zpin);
//
//zero_G is the reading we expect from the sensor when it detects
//no acceleration. Subtract this value from the sensor reading to
//get a shifted sensor reading.
float zero_G = 512.0;
//
//scale is the number of units we expect the sensor reading to
//change when the acceleration along an axis changes by 1G.
//Divide the shifted sensor reading by scale to get acceleration in Gs.
float scale = 102.3;
//
Serial.print(((float)x - zero_G)/scale);
Serial.print("\t");
//
Serial.print(((float)y - zero_G)/scale);
Serial.print("\t");
//
Serial.print(((float)z - zero_G)/scale);
Serial.print("\n");
//
// delay before next reading:
delay(sampleDelay);
}
How to buy
Click here to buy [ADXl335 3 axis accelormeter module]